The 5 Types of Clutches and How They Function

- F1 cars use multiplate clutches
- Dual Clutch transmissions run two clutches at once
- Paddle shifting cars use electromagnetic clutches
The internal combustion engine does indeed generate all that power, but without a clutch, there'd be no means for it to be converted into mechanical energy in order to propel the car forward. Keeping in mind that there is a wide range of engines and transmissions, it was essential for automakers to produce different types of clutches for various types of cars.
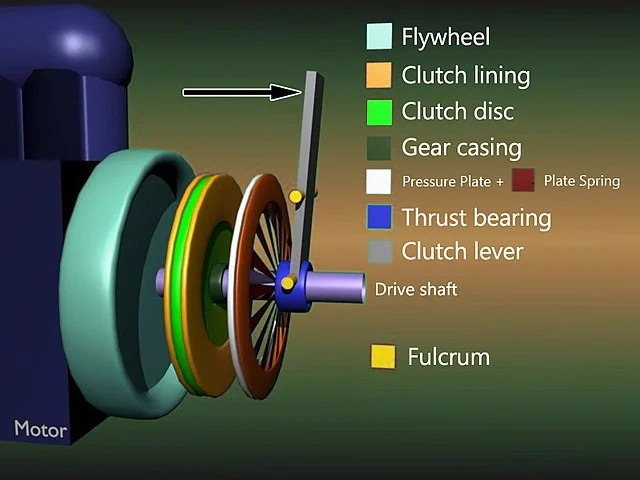
Friction Clutch

This is the most basic type of clutch and is also the most commonly used. The clutch is comprised of a release bearing, a pressure plate and a clutch plate and tends to be operated by a cable or by using hydraulics. The bearing is used to engage or disengage the flywheel and the transmission. Most cars tend to use a single plate clutch, however cars with powerful engines tend to use multiplate clutches in order to engage the transmission. Pressing the clutch pedal will disengage the transmission from the flywheel as doing so makes the bearings apply pressure to the springs on the pressure plate, in turn releasing the clutch plate.
Dry and wet clutches

Wet clutches tend to be a little more complexed. They are supplied with oil in order to keep them cool and lubricate the internals. These clutches are mostly used in machines that are high in torque figures. The heat generated from these powerful machines is what makes the oils necessary. Dry clutches however do not need any supply of lubricants or oils. Dry clutches usually tend to be single plated clutches. This in turn means that any lubrication could in fact slip the clutch due to lack of friction. Slipping in the clutch can drastically lose engine performance. This is the reason that wet clutches on the other hand tend to be multiplate clutches.
Multiplate Clutch
When a clutch has multiple plates of friction stacked one upon the other, the friction that is generated is on a much greater scale. This in turn allows it to handle a much larger torque output without sustaining any damage. The stacking of these plates enables them to fit into the same size fitment as a regular friction clutch. These clutches are mainly used for extreme high-performance motorsports such as the Formula series and the WRC respectively.
Dual Clutch mechanisms
In the premium car market segment, most cars are equipped with a dual-clutch transmission. The mechanisms comprise of using a small clutch for even gears and one large clutch for the odd ones. Due to the fast changes in gears using a DCT, they are now widely used in various types of cars such as supercars, sports cars, and even hot hatches. The fact that one clutch is engaged at all times while the other wait for input allows seamless quick shifts.
Electromagnetic and Electrohydraulic clutches
Electromagnetic clutches are usually used when there is a certain disregard for the health and life of the mechanical components that comprise the concept of shifting. This clutch setup revolves around the process of the clutch being engaged simply by proximity sensors on the shifter or the push of a button. This remote activation of the clutch comes into play through a DC current that passes through an electromagnet that in turn creates a magnetic field. These clutch systems are most common in automotive with paddle shifter systems. Pulling on any of the paddles sends an electrical signal to the clutch to disengage and engage hydraulically once shifted into the right gear. An electromagnetic clutch creates an environment where a clutch paddle is not needed at all.
Latest News
 car&bike Team | Jan 20, 2026Bajaj Pulsar 125 Updated With LED Headlamp, Indicators; Prices Start From Rs 89,910Updates are limited to the Pulsar 125 Carbon Fibre series.1 min read
car&bike Team | Jan 20, 2026Bajaj Pulsar 125 Updated With LED Headlamp, Indicators; Prices Start From Rs 89,910Updates are limited to the Pulsar 125 Carbon Fibre series.1 min read Seshan Vijayraghvan | Jan 20, 2026All-Electric Toyota Urban Cruiser EBella Introduced; Booking Open For Rs. 25,000Prices for the Toyota Urban Cruiser eBella are yet to be announced, but bookings are open at Rs. 25,000.1 min read
Seshan Vijayraghvan | Jan 20, 2026All-Electric Toyota Urban Cruiser EBella Introduced; Booking Open For Rs. 25,000Prices for the Toyota Urban Cruiser eBella are yet to be announced, but bookings are open at Rs. 25,000.1 min read Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 20, 2026Skoda Kodiaq RS India Launch In Q2 2026; Additional 100 Units Of Octavia RS India-BoundAside from debuting the facelifted Kushaq in India, Skoda had some big product announcements for the year, including a second batch of Octavia vRS and the new Kodiaq vRS.2 mins read
Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 20, 2026Skoda Kodiaq RS India Launch In Q2 2026; Additional 100 Units Of Octavia RS India-BoundAside from debuting the facelifted Kushaq in India, Skoda had some big product announcements for the year, including a second batch of Octavia vRS and the new Kodiaq vRS.2 mins read Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 20, 20262026 Skoda Kushaq Facelift Revealed With New Tech, Powertrain Updates2026 Kushaq gets a notable styling refresh, new features and a new 8-speed automatic gearbox option for the 1.0 TSI engine.3 mins read
Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 20, 20262026 Skoda Kushaq Facelift Revealed With New Tech, Powertrain Updates2026 Kushaq gets a notable styling refresh, new features and a new 8-speed automatic gearbox option for the 1.0 TSI engine.3 mins read car&bike Team | Jan 19, 2026Skoda Kushaq Facelift Debut Tomorrow: What To ExpectFacelifted Kushaq to get updated looks and new tech inside the cabin.1 min read
car&bike Team | Jan 19, 2026Skoda Kushaq Facelift Debut Tomorrow: What To ExpectFacelifted Kushaq to get updated looks and new tech inside the cabin.1 min read Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 17, 20262026 Tata Punch Facelift Price, Variants ExplainedUpdated Punch is available in 8 trim levels with naturally aspirated petrol, CNG and turbo-petrol engine options.3 mins read
Jaiveer Mehra | Jan 17, 20262026 Tata Punch Facelift Price, Variants ExplainedUpdated Punch is available in 8 trim levels with naturally aspirated petrol, CNG and turbo-petrol engine options.3 mins read
 Amaan Ahmed | Jan 17, 2026Bajaj Chetak C25 First Ride Review: Basic, Likeable E-Scooter For First-Time RidersThe Chetak C25, in quite a few ways, is poles apart from the larger and more powerful 30 and 35 Series models, but in its mannerisms, it is very much a Chetak.8 mins read
Amaan Ahmed | Jan 17, 2026Bajaj Chetak C25 First Ride Review: Basic, Likeable E-Scooter For First-Time RidersThe Chetak C25, in quite a few ways, is poles apart from the larger and more powerful 30 and 35 Series models, but in its mannerisms, it is very much a Chetak.8 mins read Bilal Firfiray | Jan 9, 2026Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder: 10,000 km Long-Term ReviewAfter spending over three months and 10,000 km with the Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder Hybrid, we were impressed by its real-world mileage, seamless hybrid, practical comfort, and Toyota reliability. Is it the best C-SUV then?5 mins read
Bilal Firfiray | Jan 9, 2026Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder: 10,000 km Long-Term ReviewAfter spending over three months and 10,000 km with the Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder Hybrid, we were impressed by its real-world mileage, seamless hybrid, practical comfort, and Toyota reliability. Is it the best C-SUV then?5 mins read Seshan Vijayraghvan | Jan 8, 20262026 Mahindra XUV 7XO Review: Big On Tech, Bigger On ComfortThe new Mahindra XUV 7XO is flashier, feature packed, and comes with more advanced tech. But are the changes just incremental or actually substantial?1 min read
Seshan Vijayraghvan | Jan 8, 20262026 Mahindra XUV 7XO Review: Big On Tech, Bigger On ComfortThe new Mahindra XUV 7XO is flashier, feature packed, and comes with more advanced tech. But are the changes just incremental or actually substantial?1 min read Preetam Bora | Jan 10, 2026Simple One Gen 2 First Ride Review: 265 km Claimed Range!The Gen 2 model of Simple Energy’s first electric scooter gets a fair few updates, including new features, tech, more range and lighter weight. We spent a couple of hours with the Simple One Gen 2 to find out if it manages to impress.6 mins read
Preetam Bora | Jan 10, 2026Simple One Gen 2 First Ride Review: 265 km Claimed Range!The Gen 2 model of Simple Energy’s first electric scooter gets a fair few updates, including new features, tech, more range and lighter weight. We spent a couple of hours with the Simple One Gen 2 to find out if it manages to impress.6 mins read Amaan Ahmed | Jan 3, 2026VLF Mobster 135 300 KM Review: Fun But FlawedA 125 cc scooter with Italian design and Chinese genes is a rare combination, and while some may be tempted to dismiss it because of its origins, the VLF Mobster shows 125s can also be exciting – but not without compromises.11 mins read
Amaan Ahmed | Jan 3, 2026VLF Mobster 135 300 KM Review: Fun But FlawedA 125 cc scooter with Italian design and Chinese genes is a rare combination, and while some may be tempted to dismiss it because of its origins, the VLF Mobster shows 125s can also be exciting – but not without compromises.11 mins read






















































































































